Search Results for: molecular formula
Molecular formula
molecular formula --> empirical formula In chemistry, a formula indicating the kind and number of atoms in the molecules... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
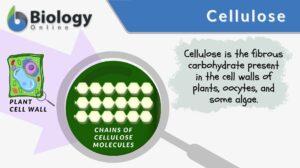
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
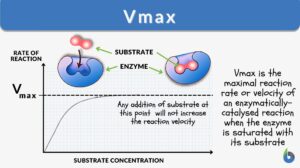
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Dansyl chloride
Definition noun (chemistry) A strongly fluorescent compound that will react with the terminal amino group of a protein;... Read More
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
Bradykinin
Definition noun A nonapeptide that is vasoactive causing blood vessels to dilate Supplement Bradykinin is a type of kinin.... Read More
Demecolcine
Definition noun (cytogenetics) A cytotoxic alkaloid isolated from Colchicum autumnale, and is used as an antineoplast... Read More
Chlorophyll a
Definition noun A type of chlorophyll that is most common and predominant in all oxygen-evolving photosynthetic organisms... Read More
Chlorophyll c
Definition noun A form of chlorophyll that occurs only in algae, specifically the diatoms, dinoflagellates and brown algae.... Read More
Chlorophyll d
Definition noun A type of chlorophyll found in marine red algae and cyanobacteria, and absorbs the infrared light of the... Read More
Immunoglobulin A
Definition noun An immunoglobulin (antibody) that is characterized by its α-heavy chain, and its prevalence in mucous... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Hyaluronic acid
Definition noun A linear mucopolysaccharide that is a major component of tissues, such as connective, epithelial and neural... Read More
SENI Biometric Analysis on the extinct Scincidae species: Macroscincus coctei (underlined)
Brian L. Schnirel Leeway Corucia Research Center (LCRC) Courtesy: Polyphemos (2004) Introduction: It has been... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More